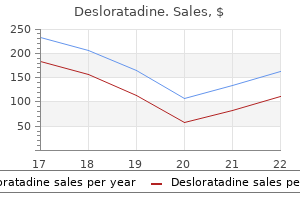
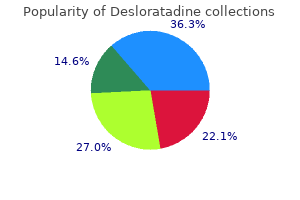
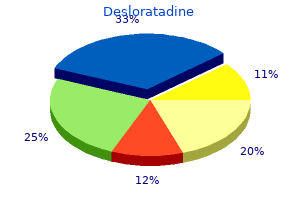
|
"Buy cheap desloratadine 5 mg online, allergy medicine 7 month old". I. Will, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D. Co-Director, University of Hawaii at Manoa John A. Burns School of Medicine
Some of the commonly available biologics or regenerative medicine therapies available to equine practitioners will be discussed below allergy symptoms newborn discount 5 mg desloratadine with visa. Cell-Based Therapies "Stemness" is a property that refers to an undifferentiated cell capable of self-renewal allergy testing kits for physicians generic desloratadine 5mg mastercard, or the ability to give rise to indefinitely more "stem" cells allergy medicine 7 year program order 5mg desloratadine with visa, and from which other specialized cell types arise by differentiation allergy medicine 018 quality 5 mg desloratadine. Although allogenic cells have advantages in terms of characterization and off-the-shelf availability, there is evidence that allogeneic stem cells are not completely "immune privileged". However, autologous cells must be culture-expanded to generate a sufficient number of cells for therapeutic applications, and this may delay treatment for 4 to 6 weeks. Initially, stem cells were though to repair tissue by engraftment and proliferation to directly replace damaged or lost cells from that tissue to be treated. For this reason, new research is focusing on the stem cell "secretome", or the paracrine (cell-to-cell communication) soluble factors produced by stem cells that promote healing. Stem cells have been shown to secrete exosomes, or extracellular vesicles, that contain many pro-growth and anti-inflammatory factors that have yet to be fully characterized. There is evidence both for and against the use of stem cell therapy for the treatment of tendon/ligament and joint disease in horses. Gene therapy is currently being employed to treat medical conditions in humans for which no other effective treatments are available; however, many gene therapy approaches are still experimental and are being investigated in clinical trials. There are no gene therapy approaches currently approved for equine musculoskeletal disease; however, experimental research into gene therapy for joint disease and tendon and ligament injuries is currently underway. Comparative effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating knee joint cartilage degenerative pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review With Quantitative Synthesis. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopedic therapy: a comparative systematic review of clinical and experimental data in equine and human musculoskeletal lesions. Effect of Leukocyte Concentration on the Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Clinical, biochemical, and histologic effects of intra-articular administration of autologous conditioned serum in horses with experimentally induced osteoarthritis. Evaluation of a single intra-articular injection of autologous protein solution for treatment of osteoarthritis in horses. Concentrated bone marrow aspirate improves fullthickness cartilage repair compared with microfracture in the equine model. Minimally Manipulated Bone Marrow Concentrate Compared with Microfracture Treatment of Full-Thickness Chondral Defects. Cell-Based Therapies for Joint Disease in Veterinary Medicine: What We Have Learned and What We Need to Know. Practical considerations for clinical use of mesenchymal stem cells: From the laboratory to the horse. Treatment of experimental equine osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the equine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. The majority of musculoskeletal fatalities are localized to the metacarpo- and metatarsophalangeal (fetlock) joints. While veterinarians, horse owners and horse trainers have made strides in reducing the number of pelvic and proximal limb stress fractures. Proximal limb fractures have been shown to be a result of stress-induced bone injury, and we are more likely to detect proximal limb stress fractures because many horses show evidence of prodromal lameness before the catastrophic fracture occurs. Unfortunately, lameness is often not present or not detected in horses prior to sustaining catastrophic fetlock fractures. The detection of sub-clinical lameness in racehorses is currently the subject of several ongoing studies using objective gait analysis techniques at racetracks in Singapore and Hong Kong. Horse-related factors with strong evidence included: older age and older age at first start, male sex, higher race class and lower claiming price. Race-related factors included: firm turf-track conditions, wet dirt-track conditions, longer race distance and greater number of starters in a race. Management-related factors included: greater time between starts, greater number of starts, longer racing career, abnormal pre-race examination findings, previous injury and recent administration of medication to horses.
Calcium bioavailability is inhibited by phytate (found in high-fibre cereals allergy treatment without antihistamines order 5 mg desloratadine overnight delivery, legumes and seeds) and oxalate (found in fruit allergy forecast thunder bay order desloratadine 5 mg amex, vegetables allergy forecast grand prairie tx generic desloratadine 5 mg, legumes and grains) content of food allergy shots ok during pregnancy order desloratadine 5 mg with visa. Iron the clinical incidence of iron deficiency anaemia is no greater in vegetarian children than in omnivores, although iron stores tend to be lower [11]. Phytate, soy protein and polyphenols/tannins can inhibit iron absorption, while several nutrients, including vitamin C, retinol and carotenes, can enhance the Vegetarian Diets 137 wrn367873. Dietary advice should encourage a variety of non-haem iron sources (as shown in table 2) and vitamin C with meals to aid iron absorption. Food preparation methods such as soaking beans prior to cooking and fermenting soy protein. Zinc Zinc deficiency can cause failure to thrive and impaired taste acuity in children [11, 12]. The main sources of zinc in vegetarian diets include cereals and grains, which are also high in phytate and reduce zinc bioavailability [10]. Differences in zinc intake between vegetarian and omnivorous children are negligible [11]. However, the ratio of phytate to zinc intake is much greater in vegetarian children, which can increase the risk of suboptimal zinc status especially during periods of rapid growth [11, 12]. Little is known regarding the effects of marginal zinc deficiency on childhood growth and development, although adaptation to a low intake may occur over time with increased intestinal absorption [11]. Malnutrition is defined as a deviation from the normal state of nutrition; it can logically be either undernutrition or overnutrition (overweight and obesity). A deficiency in proper nutritional elements due to any cause leads to undernutrition. Undernutrition is a broad term ranging from restricted intrauterine growth, low birth weight, stunting, wasting and underweight to micronutrient deficiencies. It is the outcome of suboptimal dietary intake, metabolic stress, malabsorption and increased nutrient demands. Undernutrition may develop either because people cannot access proper food or have an underlying disorder that limits eating or absorbing consumed food. In the context of lowand middle-income countries, where overnutrition is relatively less prevalent, malnutrition commonly implies stunting, wasting and/or underweight. Primary malnutrition in children is most commonly seen in low- and middle-income countries. The factors responsible for primary malnutrition include household food insecurity, poverty, poor nutrition of women during pregnancy, intrauterine growth restriction, low birth weight, poor breastfeeding and inappropriate complementary feeding, frequent infectious illnesses, poor quality of water, sanitation and hygiene, etc. Although there is enough food in the world to feed all, it is sad to see hunger and malnutrition ravage through many countries primarily because of inequity and inequality affecting access to nutritious food. The problem of primary malnutrition is, therefore, mostly social rather than biomedical in origin. A child who is repeatedly exposed to pathogens in the environment has bacterial colonization of the small intestine. There is an increased accumulation of inflammatory cells in the small intestinal mucosa, the intestinal villi are damaged and distorted by the inflammatory process, and, consequently, they malabsorb nutrients, which results in malnutrition. Secondary malnutrition, in contrast, results from an underlying disease that compromises growth directly or through its deleterious effect on appetite or the absorption of nutrients. Infectious illnesses result in malnutrition by reducing the intake of nutrients and their bioavailability, by increasing nutrient and energy expen- diture and by diverting nutrients away from growth. In patients with extensive burns, increased catabolism, anorexia and loss of plasma proteins from the exposed skin surfaces lead to malnutrition.
Myosin molecules can aggregate into bundles allergy testing essex desloratadine 5mg sale, each bundle consisting of a number of longitudinally adjacent molecules arranged so that head regions occur at each end allergy shots dosage schedule generic desloratadine 5 mg visa. The cells are spherical allergy skin rash generic desloratadine 5mg visa, and each contains a single cup-shaped chloroplast with no pyrenoid; autospores and zoospores may be formed allergy symptoms under eyes desloratadine 5 mg low price. Chondromyces, Nannocystis, Polyangium) the myxospores resemble Myxomycetes vegetative cells, while in others. Myxococcus, Stigmatella) they are shorter, or spherical, and refractile; in at least some genera. Archangium, Myxococcus xanthus) the fruiting body is merely a small, sessile (non-stalked), rounded or irregularly shaped mound of myxospores set in slime; in M. In many genera the myxospores are enclosed within one or more hard, sac-like structures termed cysts or sporangia. In Nannocystis individual sporangia are embedded in the substrate, while in Cystobacter and Polyangium the fruiting body consists of a single sessile sporangium or a group of sessile sporangia; in Chondromyces, Melittangium and Stigmatella one or more sporangia occur on simple or branched stalks. Transmission occurs (mechanically) via arthropod vectors (rabbit fleas, mosquitoes etc), and by direct contact etc. In its natural host, Sylvilagus brasiliensis (a forest rabbit native to Brazil and Uruguay), the myxoma virus usually causes only a localized lesion. Sexual reproduction occurs in most (if not all) species, and the life cycle typically exhibits alternate haploid and diploid phases. The amoeboid/flagellated cells function as gametes: cells of compatible mating type fuse, and the zygote develops into the main vegetative stage of the organism, the plasmodium. Shuttle streaming (a rapid, rhythmic, back-and-forth flow) of the protoplasm occurs in aphanoplasmodia and phaneroplasmodia; in protoplasmodia streaming is very slow and irregular. Prior to fruiting, the plasmodium generally flows out onto an exposed surface; in some species light is apparently necessary to initiate fruiting. Three major types of fruiting body are formed, in each of which the spores develop in masses within a persistent or evanescent peridium. A sporangium is a relatively small, sessile or stalked structure which is more or less uniform in size and shape for a given species; many sporangia usually develop from a single plasmodium. Meiosis is believed to occur in the maturing spores; three of the four resulting nuclei apparently degenerate. Several hundred species of myxomycetes are recognized [descriptions and illustrations: Book ref. The myxosporean spore contains between one and six (typically two) polar capsules (each containing a coiled filament), and one or two sporoplasms; the spore wall consists of two valves (order Bivalvulida. When ingested by a host animal, the spore explosively discharges its coiled filament(s), the discharged filament apparently serving to attach the organism to the gut epithelium. The amoeboid sporoplasm(s) emerges and passes through the gut wall, subsequently localizing in a particular tissue (in histozoic species. Eventually, many of the nuclei in the plasmodium each become segregated into cells (sporonts) destined to become spores; depending on species, a sporont may develop into a single spore (monosporous sporont) or into two or more spores within a common envelope (the whole being termed a pansporoblast). Cells containing somatic nuclei are involved in the formation of the spore wall, polar filament(s) and polar capsule(s), while generative nuclei are incorporated in the sporoplasm(s) (commonly two nuclei per sporoplasm). The mature spores may be released into the bloodstream or may remain in situ until the host is eaten. The organisms form spores of multicellular origin; a spore contains one or more extrusile polar filaments, each coiled within a separate sac (the polar capsule), and one or more sporoplasms (amoeboid cells which are the infective forms of the organism). N-end rule the observed relationship between the N-terminal amino acid of a protein and the half-life of that protein in vivo. Ascus formation follows conjugation between a bud and its mother cell; ascospores contain a prominent lipid globule and are spherical, brownish, warty or spiny, 1 or 2 per ascus.

Failure to absorb lactase results in bacterial fermentation in the colon allergy to yellow 5 symptoms buy 5mg desloratadine with amex, presenting as flatulence allergy treatment otc purchase desloratadine 5mg with visa, diarrhea allergy testing for mold buy generic desloratadine 5 mg on line, acidic stools and perianal skin excoriation [5] allergy medicine bag discount 5mg desloratadine otc. The abundance of lactase activity is genetically regulated and slowly drops after infancy (lactase nonpersistence). This often leads to symptomatic hypolactasia by adult age, particularly in non-Caucasian individuals. Primary lactose intolerance (congenital absence of lactase) in infants is rare [5]. Secondary forms of lactose intolerance may be transient and resolve after the underlying gastrointestinal condition. Breath hydrogen testing may be used to confirm the diagnosis of lactose malabsorption; however, its correlation with diet response varies [5]. In formula-fed infants, a lactosereduced formula or soy formula can be used if symptoms are significant. In cases of postenteritic lactose malabsorp- tion, breastfeeding should be continued. Incubation of expressed breast milk with lactase drops may be effective if symptoms are severe [5]. Detection of specific IgE antibodies (sensitization) on its own, in the absence of clinical symptoms, is not diagnostic (table 3). In patients with equivocal results, the diagnosis of IgE-mediated food allergy needs to be assessed by formal food challenge in hospital (due to the potential risk of anaphylaxis) [8]. No useful in vitro markers for non-IgE-mediated food allergy are currently available. The diagnosis of non-IgEmediated food allergy relies on recognition of the clinical presentation, demonstration of improvement after a 2- to 4-week period of food allergen elimination, and relapse of symptoms after a food challenge. In addition, breath hydrogen testing (lactose and fructose) and measurement of disaccharidase levels in duodenal biopsies may be useful in patients with suspected carbohydrate malabsorption syndromes (lactase or sucraseisomaltase deficiency). As allergens are commonly disguised in manufactured food products, this involves education of parents and careful reading of ingredient labels [14]. In non-IgE-mediated food allergy, due to the diverse spectrum and underlying mechanisms and the absence of clear diagnostic markers, it may be difficult to define an exact diagnosis. In these children, empirical treatment with dietary manipulations is common practice. Elimination diets avoiding multiple food allergens should be monitored by a pediatric dietician to safeguard the nutritional adequacy of the diet, and growth parameters should be carefully monitored. In breastfed infants, a maternal elimination diet may be effective as intact food antigens in breast milk can elicit allergic manifestations in the infant [9]. There are two main types of hydrolyzed formula, partially and extensively hydrolyzed formulas. These relaxations occur physiologically in all people, are more common after meals, in the sitting position, and following high-osmolarity meals. These include a dysfunctional lower esophageal sphincter (hiatal hernia, after repair of esophageal atresia, after Heller myotomy), increased intra-abdominal pressure (peritoneal dialysis, abdominal mass), cystic fibrosis, psychomotor delay, obesity, prematurity and others. Several hormones, drugs and nutrients have been implicated in influencing tone of the lower esophageal sphincter, but the clinical significance of most of these have not yet been rigorously studied. Thereafter there is a gradual decrease in prevalence, such that by around 18 months of age, reflux has resolved in the vast majority of cases. The remaining patients generally warrant investigation even if the regurgitation remains asymptomatic. Signs and Symptoms appear seizure-like or be mistaken for torticollis), and excessive crying may be seen, though none of these are specific. Older children and adolescents may present with frank regurgitation, and heartburn, noncardiac chest pain and epigastric abdominal pain may be present [6].
|
|